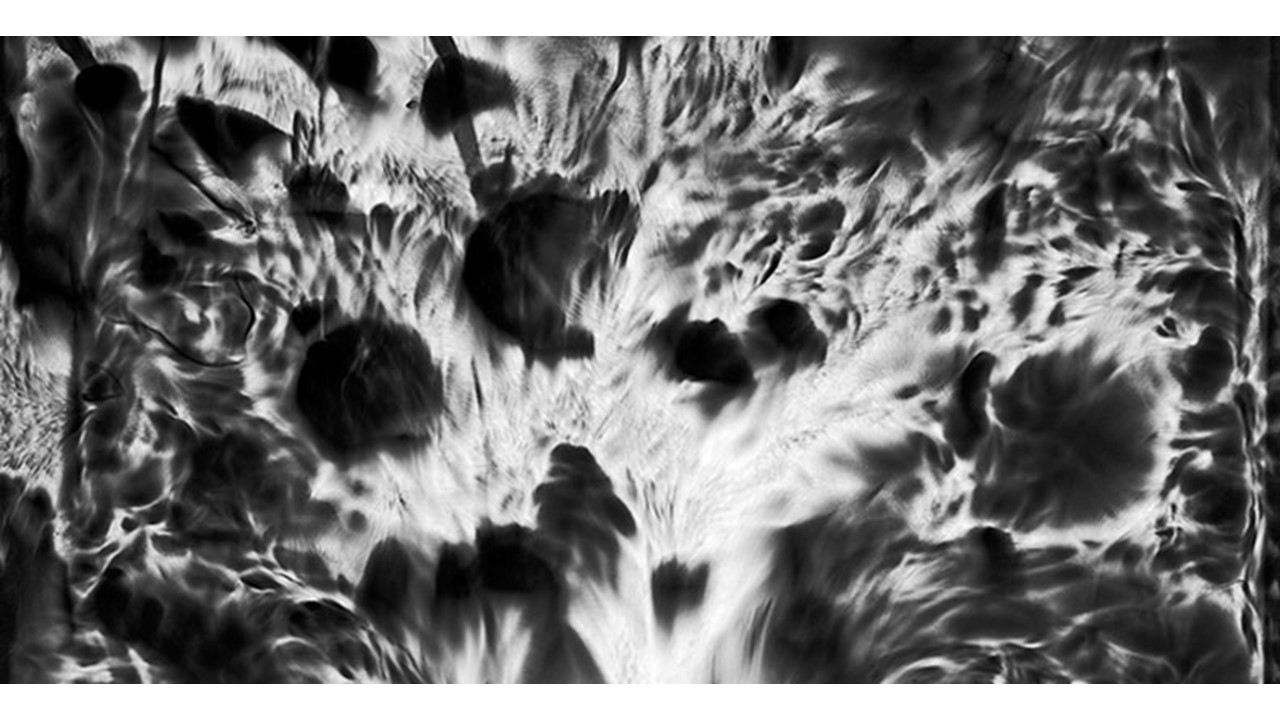
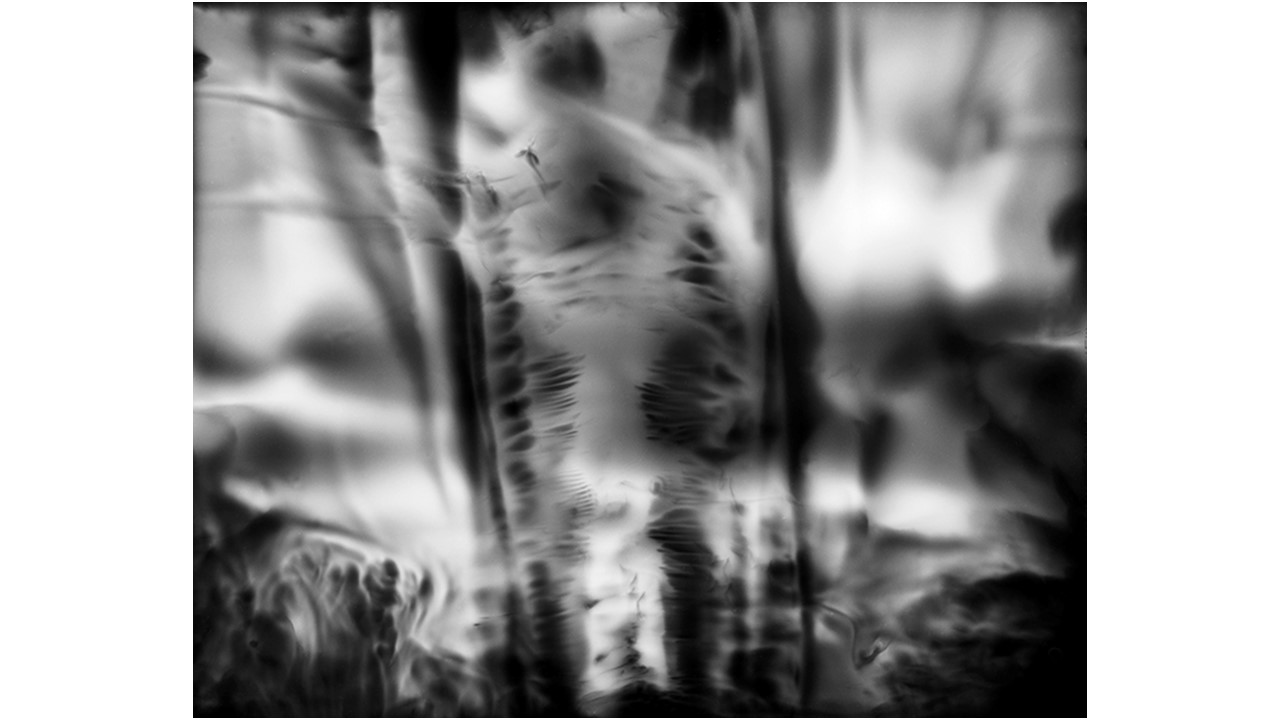
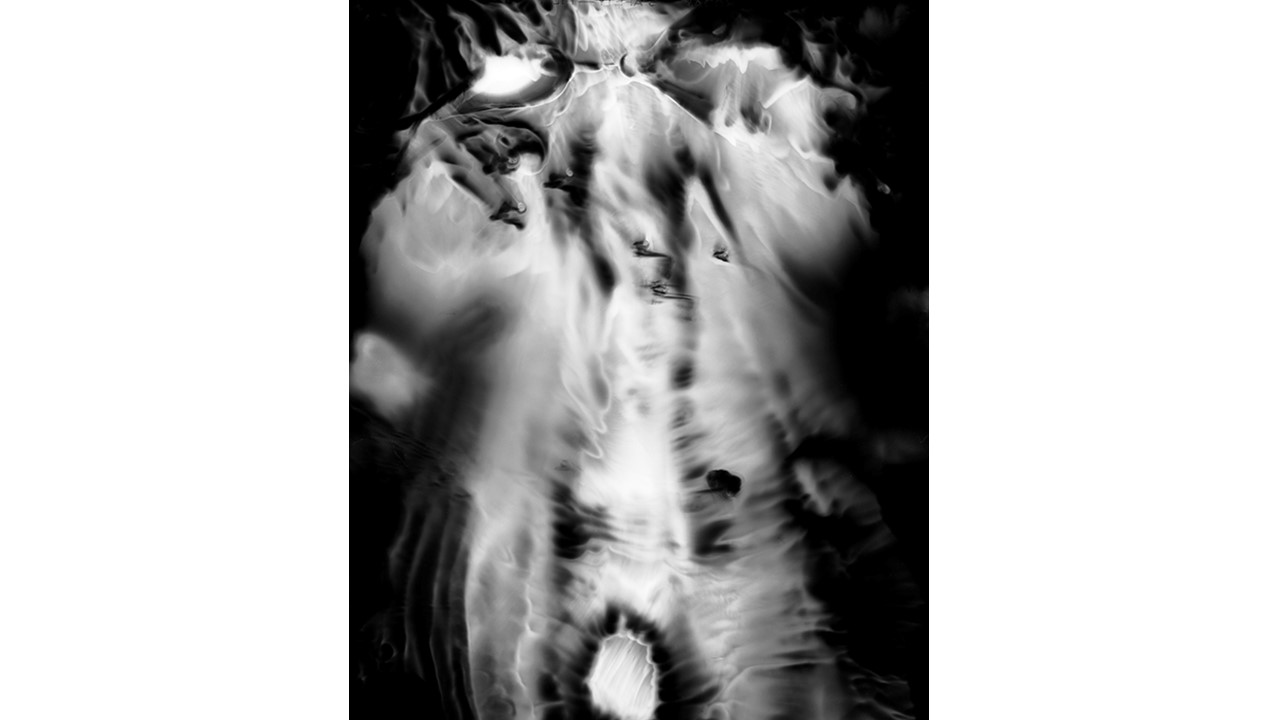
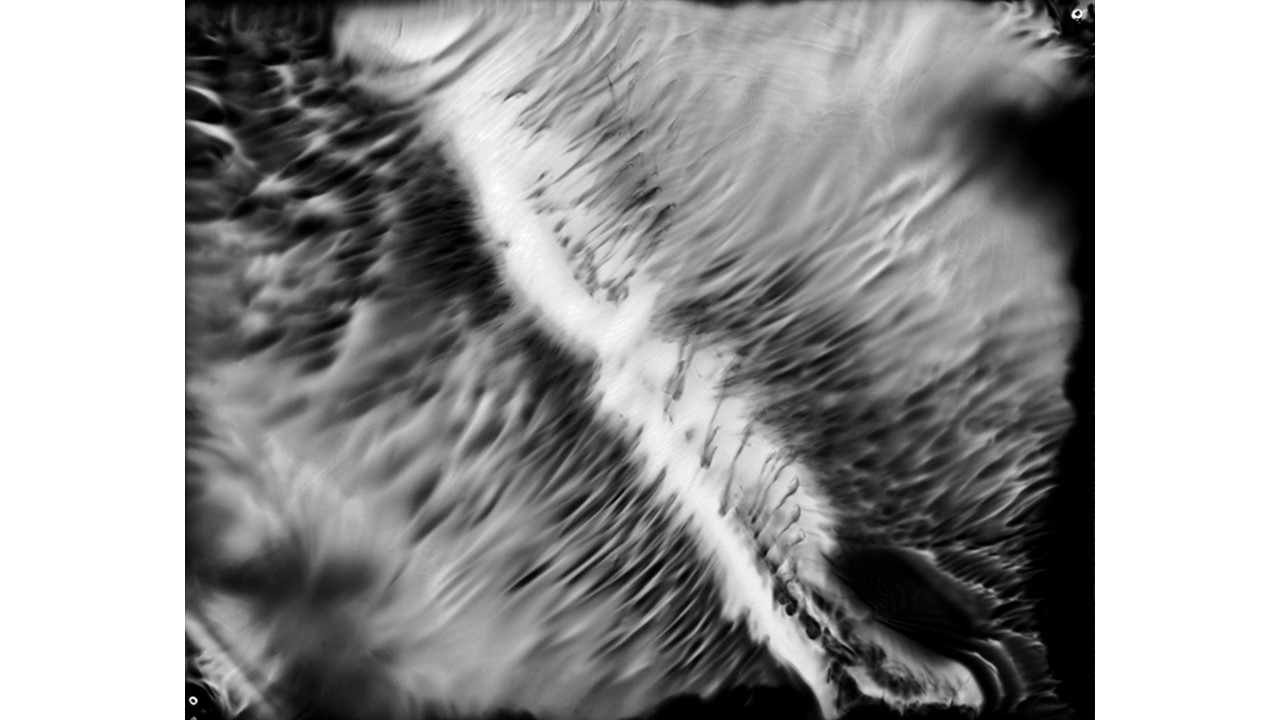
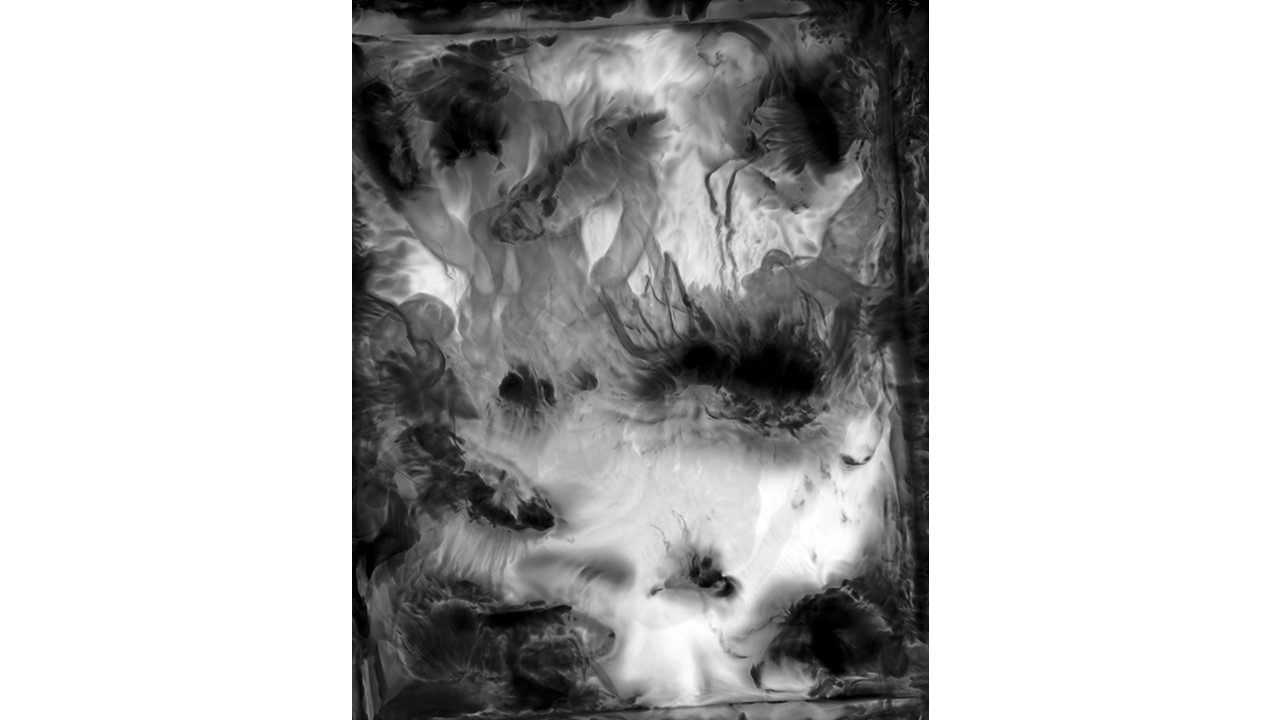
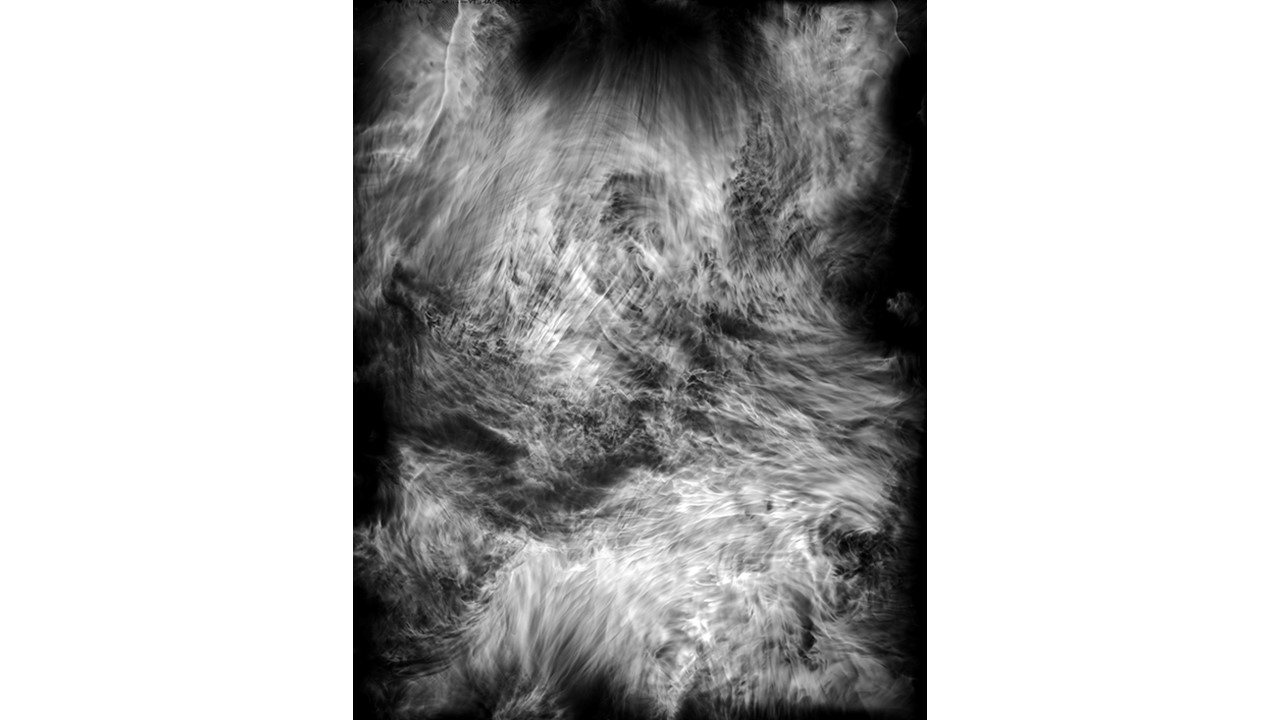
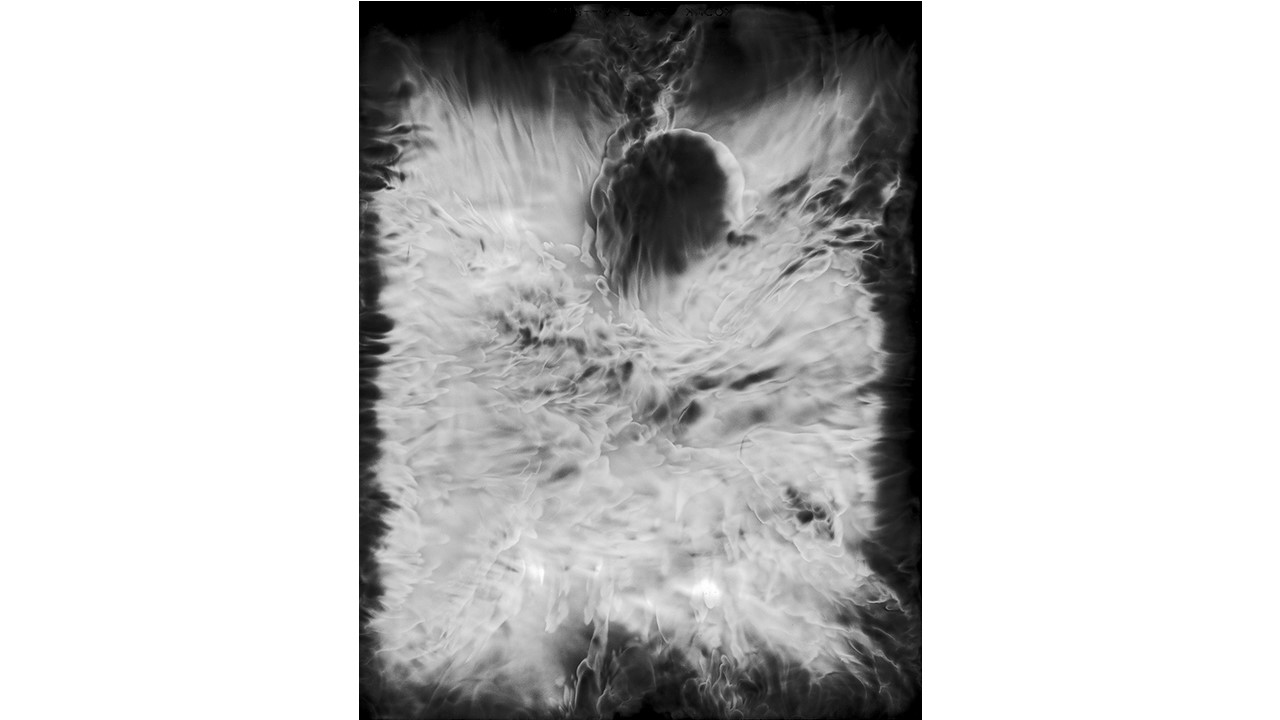
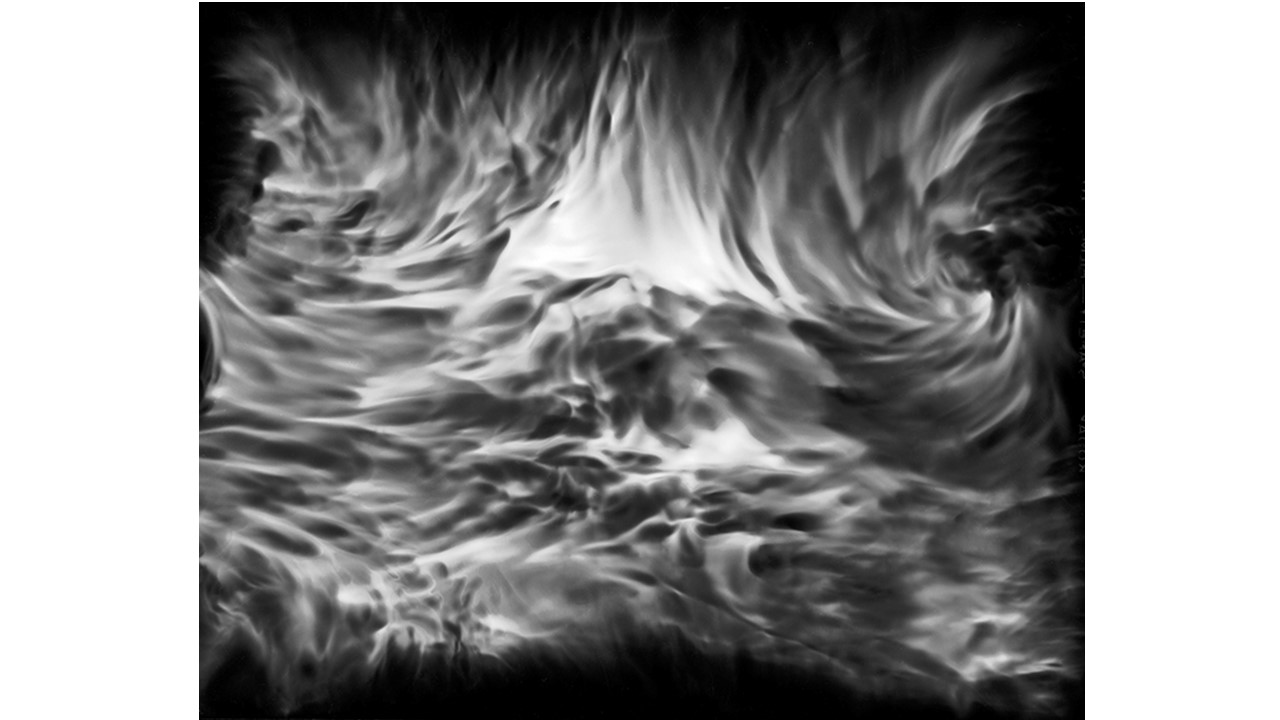
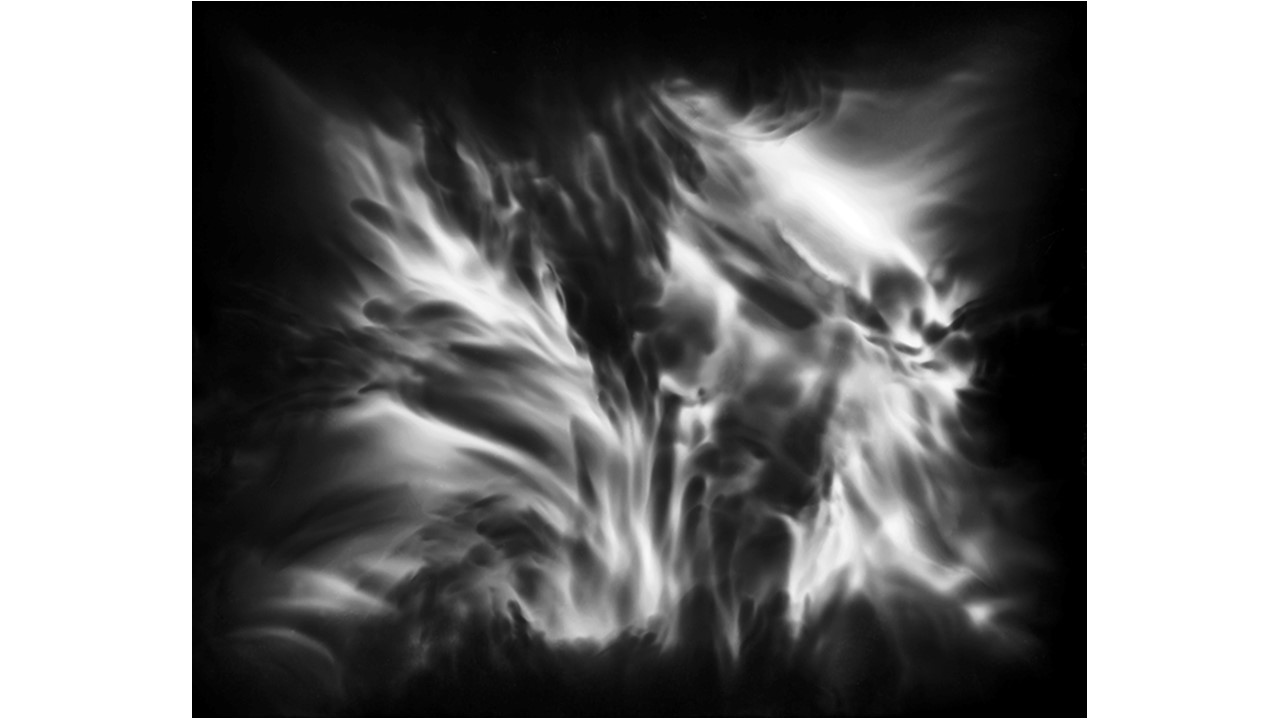
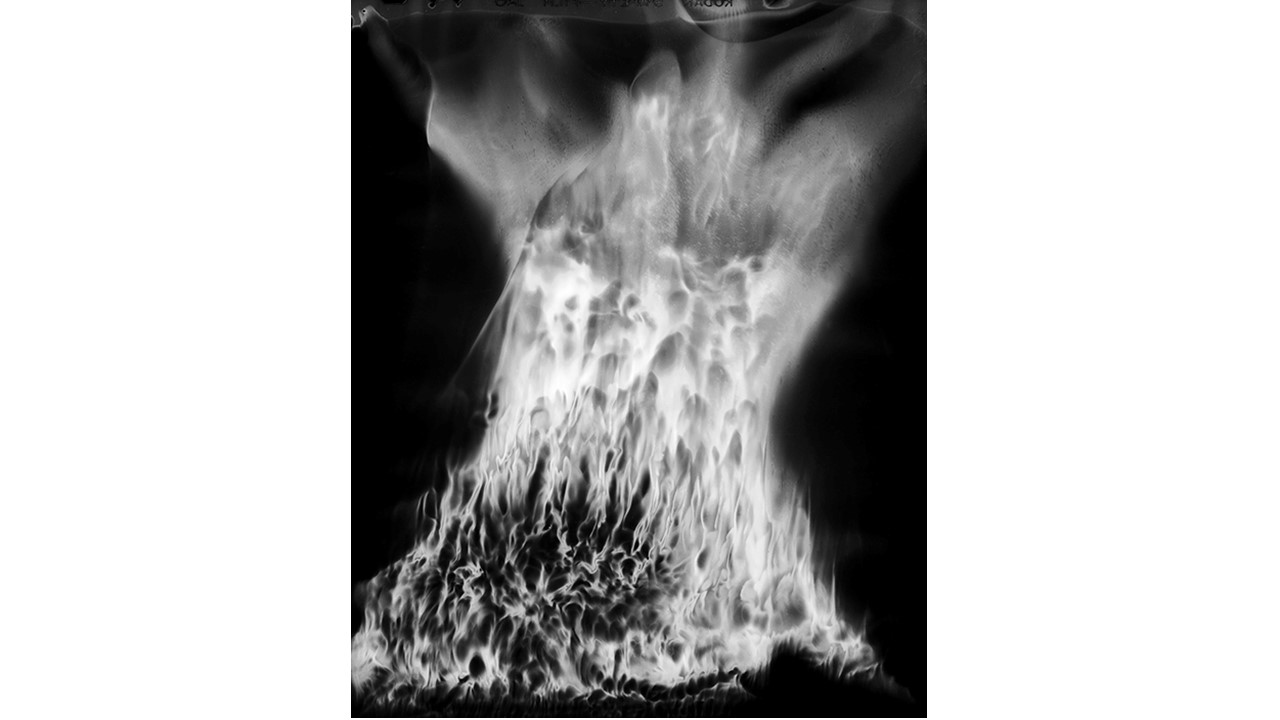
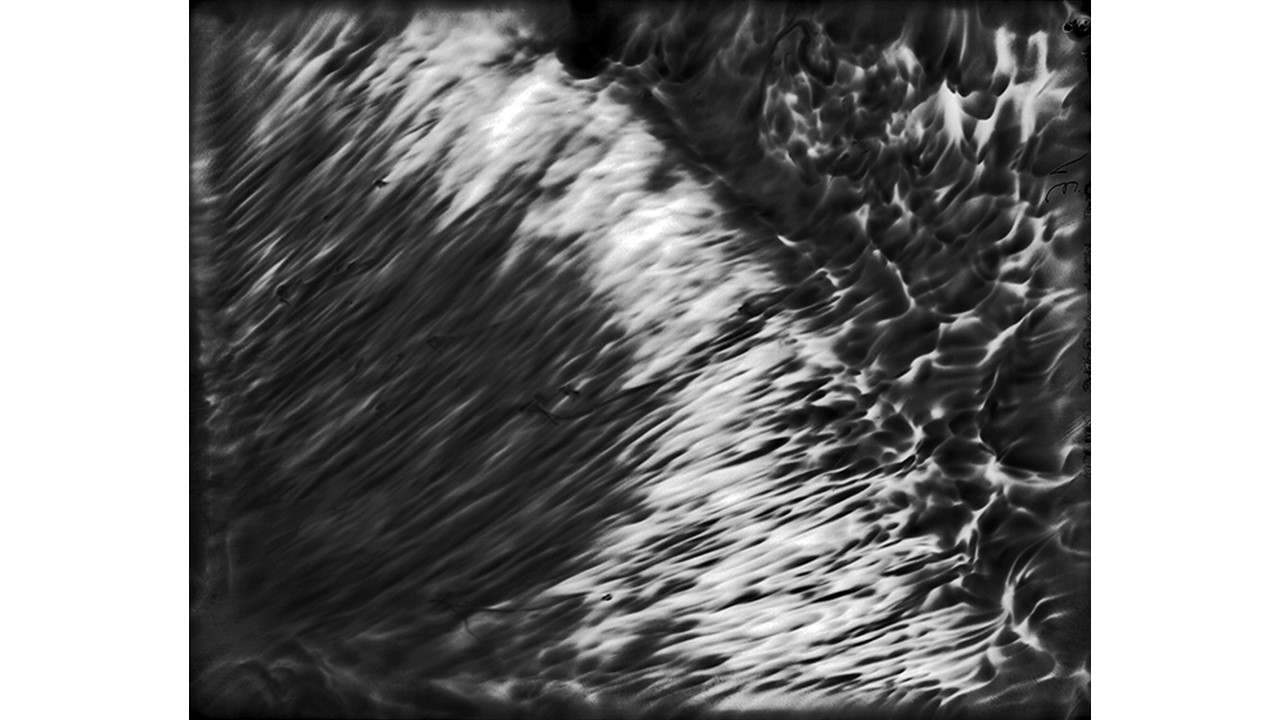
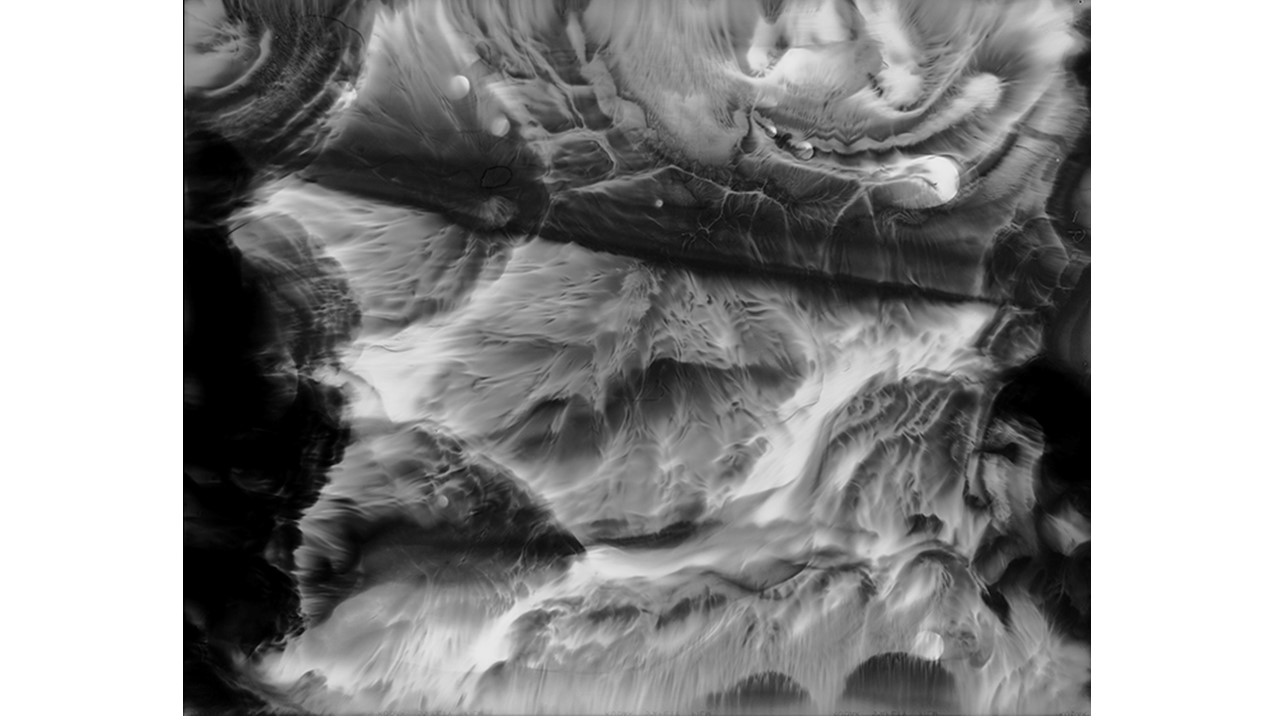
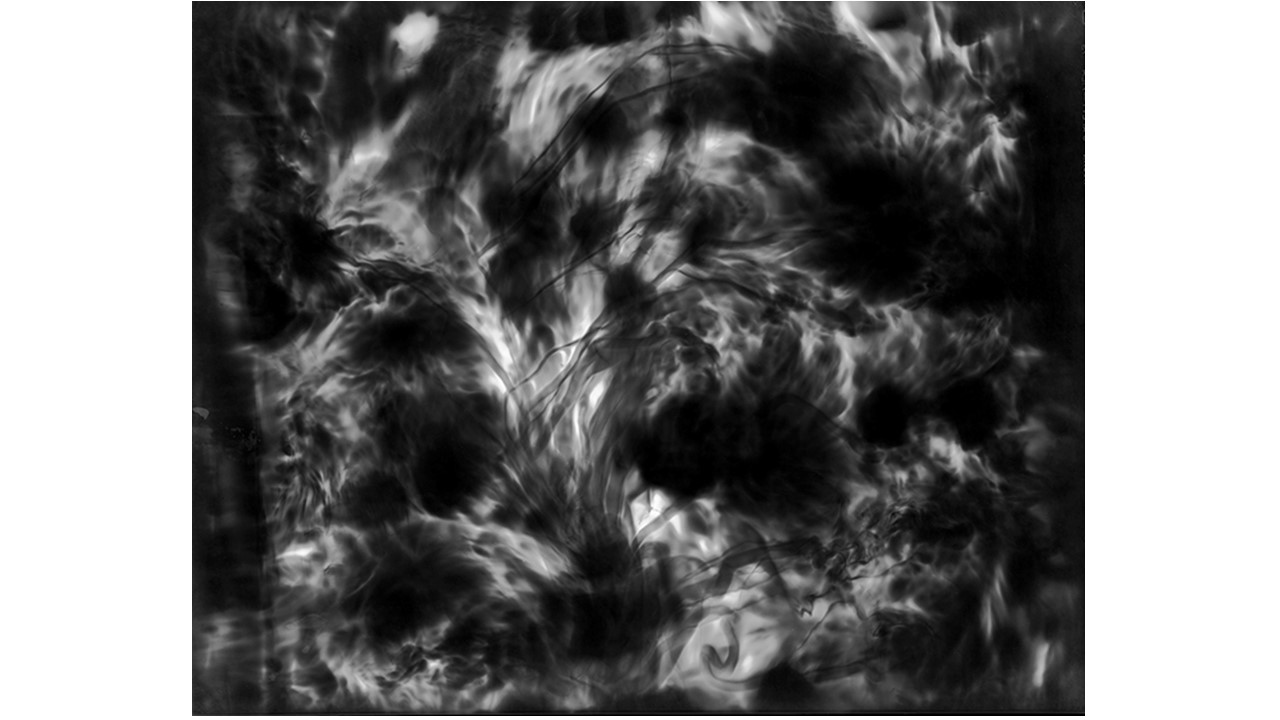
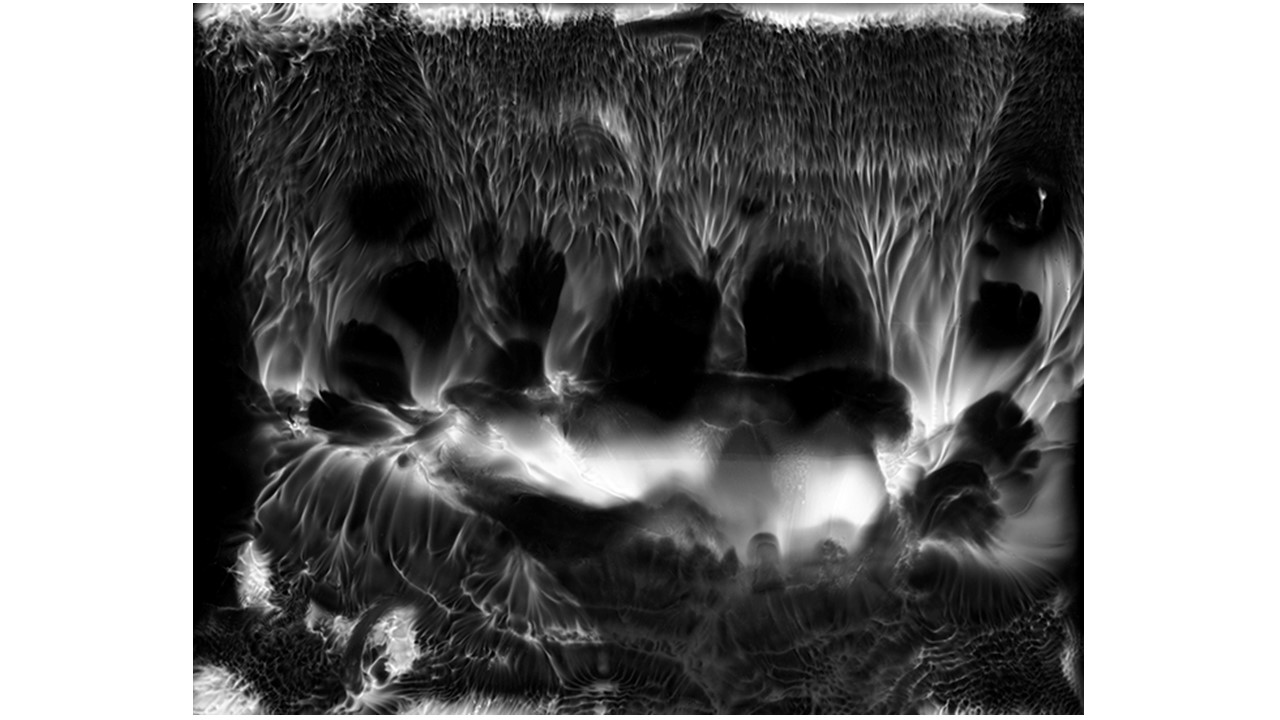
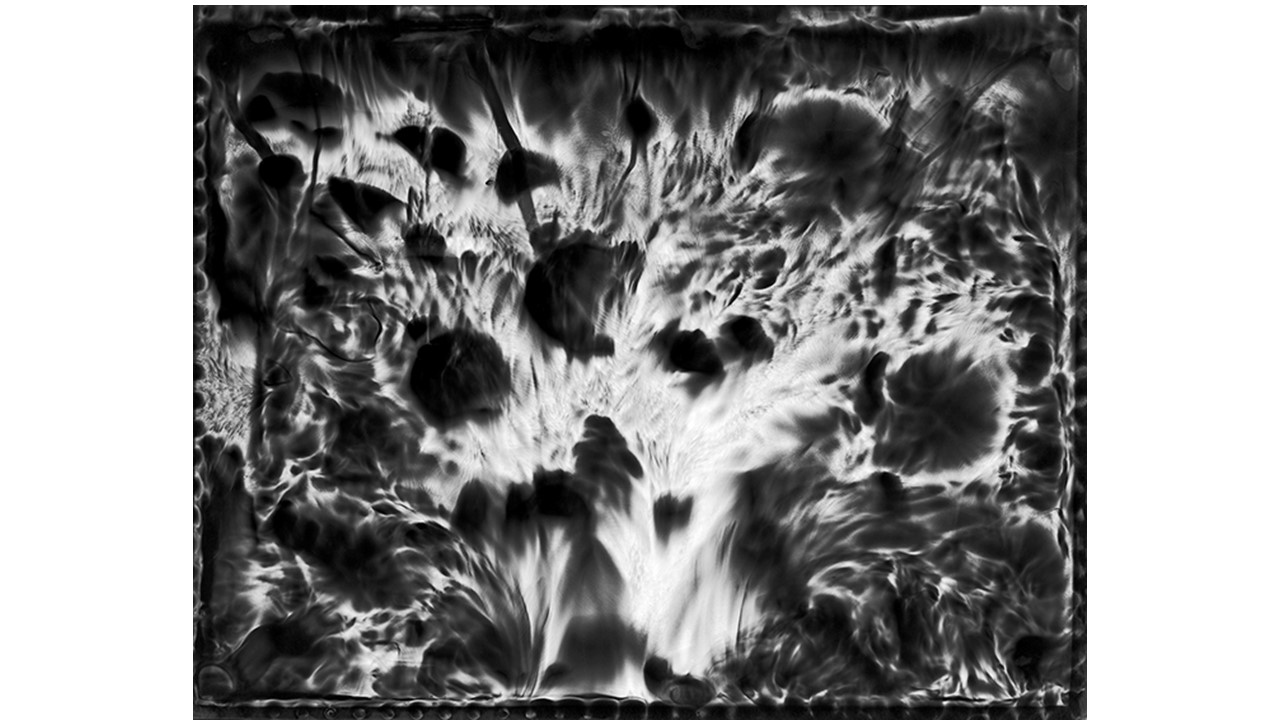
From 1967 to 1971, he carried out an experiment related to mental strength, in which he combined his skills in the field of chemistry and photography, with the power of meditation and thought, using them as an inspiring source, thus achieving an extensive production of abstract images in black and white and color, which he called Numinal Photography or Thought Photography. Photographs of abstract language, kept by the author, in strict secrecy.
"Thought that looks for traces and symbols in the luminous echo that moves and boils in us. Thought that surrounds and captures forces and essences that turn in time, and the images arrive in the current of the sidereal rivers and in the lights that are only guessed at in the solitude of infinity. A thought that penetrates the remote roots where forms and dreams are born." Armando Salas Portugal, 1968.
K. Bohmer and W. Christian, in subsequent reports, determined that menstrual blood and urine emit radiation. Irradiation that is higher in younger individuals.
Psychiatrist Braines proved that silent, indifferent schizophrenics have little irradiation; on the other hand, maniacs, or those in continuous movement, radiate intensely.
RODIONOW, AUDEBER, VAN DOORMAL, BORODIN
Rodionow, Auduber, Van Doormal, Borodin, among others, proved that all living tissues radiate energy, whether animal or vegetable. In their experiments with inorganic chemical reactions, activated by ultraviolet or solar light, they also obtained radiation.
DR. OTTO RAHN
In 1932, Dr. Otto Rahn, in a book of his authorship, compiled the experiences and studies carried out by several researchers, related to radiation. Rahn explained that certain people have the faculty of emitting radiation at will, in the range of 2,000 Angstroms, with beneficial or maleficent intentions.
S. P. SCHURIN, V. K. KAZNACHEYEV, L. MIKHAILOVA
In 1972, S. P. Schurin, V.K. Kaznacheyev, L. Mikhailova, researchers at the Nobosibirsk Institute of Experimental Medicine in Russia, described that living cells receive information through special electromagnetic radiation.
PFEIFFER
In 1955, Pfeiffer, a follower of the philosopher Steiner, studied human pathology, revealing that the blood of sick people crystallized in a characteristic way, determined by the "nosological" entity that affected the person, due to the radiation of the blood.
He obtained the crystallographic image of the blood of a sick subject; after hemolizing and adding a specific homeopathic remedy, according to the symptoms of the disease, he obtained a crystallization model similar to normal blood.
KIRLIAN SEMION
Around the 1940s, Kirlian discovered the electrographic technique to photograph the bioplasm or aura surrounding the human body. Kirlian demonstrated that alterations in the aura spectrum also discovered by electro photography, the edges of "the ghost leaf". He proceeded to cut a piece of a leaf, by means of the technique of electro photography he obtained a photo, where the original borders of the leaf were appreciated as if it was complete.
ALBERT ABRAMS
Albert Abrams, American scientist, considered the "father of Radionics".
In 1910, Dr. Abrams performed routine examinations on his patients, using a physical examination technique known as percussion.
Abrams began to perform experiments using healthy young men, which he attached by means of an electrode to the sick patients, as well as to pathological tissues, in order to diagnose various diseases.
Abrams continued to experiment with this "electronic" energy. First he had a special box built with variable resistance (in ohms units), in order to discriminate and filter the different frequencies of diseases, comparing healthy and sick patients. The method is recognized as "Abrams' electronic reaction". The instrument was the first radionic apparatus in the history of the specialty.
RUTH DROWN
Ruth Drown, a chiropractor and disciple of Dr. Abrams, also discovered a radio vision camera through which they obtained photos of diseased organs, using a drop of blood as a witness. It is believed that these photographs were obtained due to her elevated psychic perception.
In spite of the virtuous treatments obtained by the chiropractor Ruth Drown was persecuted by the political and economic power organisms, controlled by the merkava in the USA, particularly by the judicial system and the medical professionals. After a long battle in the courts of justice, she was sentenced to prison.
The persecution of Radionics practitioners reached such a point that the mere possession of a Radionic device by a doctor was punished. They were treated like any common criminal, imprisoned without a trial. Radionics became a punishable offence in some States of the American Union.